Botox is a drug that weakens or paralyzes muscle. In small doses, it can reduce skin wrinkles and help treat some medical conditions.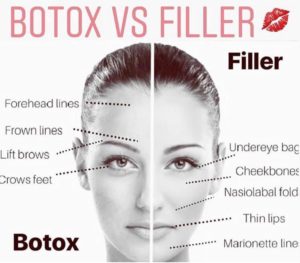
Botox is a protein made from Botulinum toxin, which the bacterium Clostridium botulinum produces. This is the same toxin that causes botulism.
Botox is a toxin, but when doctors use it correctly and in small doses, it can have benefits. It has both cosmetic and medical uses.
As a cosmetic treatment, Botox injections can reduce the appearance of skin wrinkles.
Also, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have approved it as a treatment for various health issues, including eyelid spasms, excessive sweating, some bladder disorders, and migraine.
Commercial preparations of Botulinum toxin include:
People casually use the term “Botox” to describe all of these products, though Botox is a registered trademark that one company owns.
Botox is a neurotoxin. These substances target the nervous system, disrupting the nerve signaling processes that stimulate muscle contraction. This is how the drug causes temporary muscle paralysis.
In order for any muscle to contract, the nerves release a chemical messenger called acetylcholine at the junction where nerve endings meet muscle cells. Acetylcholine attaches to receptors on the muscle cells and causes the cells to contract, or shorten.
Botox injections prevent the release of acetylcholine, which stops the muscle cells from contracting. In this way, the toxin helps the muscles to become less stiff.
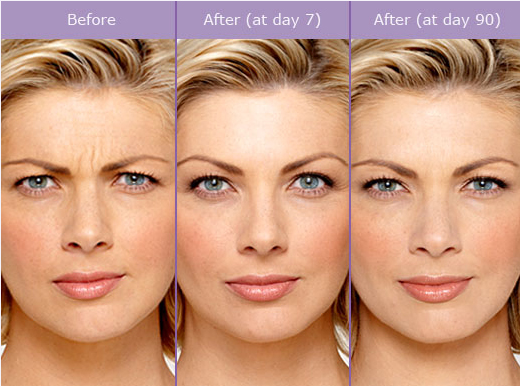
The primary use of Botox is reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles.
According to the American Board of Cosmetic Surgery, Botox injections are the most popular cosmetic procedure nationwide. In 2016, over 7 million people had Botox treatments.
The effects are temporary, lasting 3–12 months, depending on the type of treatment.
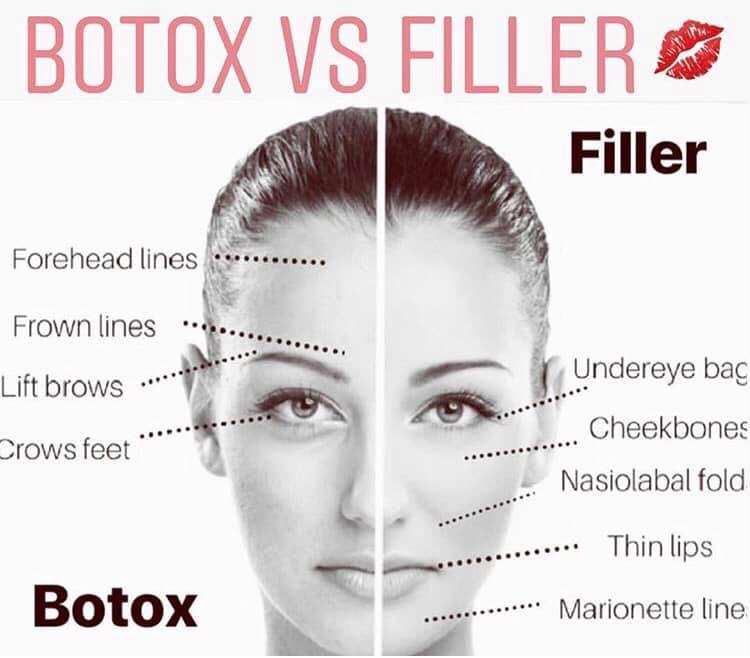
People often request the injections in the following areas of the face to reduce the wrinkles:
CClinicians use Botulinum toxin by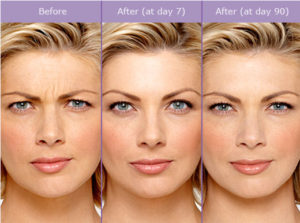 diluting the powder in saline and injecting it directly into neuromuscular tissue.
diluting the powder in saline and injecting it directly into neuromuscular tissue.
It takes 24–72 hours for the toxin to take effect. Rarely, it can take as long as 5 days for the full effects to show. They may last 3–12 months, depending on the treatment.
With topical anesthetic, a Botox procedure can be virtually painless.
Even without a numbing agent, pain is minimal, and you may only feel a little pinch. Injections are very quick and with a trained medical professional, you may not even notice when they happen.
Many people associate pain with Botox because of a fear of needles or bad memories of getting vaccines.
But you will be happy to know that Botox needles are tiny. In fact, they are about the same size needle that diabetics use to self-inject themselves with insulin.
One common side effect of Botox is minimal bruising, which can be tender but will go away shortly.
Botox is a drug that weakens or paralyzes muscle. In small doses, it can reduce skin wrinkles and help treat some medical conditions.
Botox is a protein made from Botulinum toxin, which the bacterium Clostridium botulinum produces. This is the same toxin that causes botulism.
Botox is a toxin, but when doctors use it correctly and in small doses, it can have benefits. It has both cosmetic and medical uses.
As a cosmetic treatment, Botox injections can reduce the appearance of skin wrinkles.
Also, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have approved it as a treatment for various health issues, including eyelid spasms, excessive sweating, some bladder disorders, and migraine.
Commercial preparations of Botulinum toxin include:
People casually use the term “Botox” to describe all of these products, though Botox is a registered trademark that one company owns.
Botox is a neurotoxin. These substances target the nervous system, disrupting the nerve signaling processes that stimulate muscle contraction. This is how the drug causes temporary muscle paralysis.
In order for any muscle to contract, the nerves release a chemical messenger called acetylcholine at the junction where nerve endings meet muscle cells. Acetylcholine attaches to receptors on the muscle cells and causes the cells to contract, or shorten.
Botox injections prevent the release of acetylcholine, which stops the muscle cells from contracting. In this way, the toxin helps the muscles to become less stiff.
The primary use of Botox is reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles.
According to the American Board of Cosmetic Surgery, Botox injections are the most popular cosmetic procedure nationwide. In 2016, over 7 million people had Botox treatments.
The effects are temporary, lasting 3–12 months, depending on the type of treatment.
People often request the injections in the following areas of the face to reduce the wrinkles:

Clinicians use Botulinum toxin by diluting the powder in saline and injecting it directly into neuromuscular tissue.
It takes 24–72 hours for the toxin to take effect. Rarely, it can take as long as 5 days for the full effects to show. They may last 3–12 months, depending on the treatment.
With topical anesthetic, a Botox procedure can be virtually painless.
Even without a numbing agent, pain is minimal, and you may only feel a little pinch. Injections are very quick and with a trained medical professional, you may not even notice when they happen.
Many people associate pain with Botox because of a fear of needles or bad memories of getting vaccines.
But you will be happy to know that Botox needles are tiny. In fact, they are about the same size needle that diabetics use to self-inject themselves with insulin.
One common side effect of Botox is minimal bruising, which can be tender but will go away shortly.